Generate a sample from Analytics Hub
Each analytic test in the Analytics Hub includes a sample calculator in the Test Parameters tab. This tool lets you generate Random, Attribute, or Monetary Unit samples. You can also apply Systematic sampling manually, without the calculator. Sampling helps you quickly gain insights from large datasets by analyzing a smaller, representative portion, whether you're working with structured data like client transactions or unstructured inputs such as natural language descriptions (for example, 'Monthly control = bank reconciliations are reviewed and approved by the Controller'). You can use sampling within an analytic test or as a standalone tool.
Sampling methods
The following sampling methods are available:
Attribute sampling
Attribute sampling is a statistical method used to evaluate the frequency of a specific attribute within a dataset. Each attribute is binary, having only two possible outcomes: true or false, and is commonly used for testing controls or compliance.
Monetary unit sampling
Monetary unit sampling (MUS) selects records based on the monetary value of a specified column. Each monetary unit (for example, each dollar) is treated as a sampling unit, giving larger transactions a higher probability of selection compared to smaller ones. The sample size is determined by parameters, such as risk tolerances and confidence levels. This method is especially useful in financial auditing, as it focuses on transactions with greater monetary impact. MUS is applicable to both the general ledger and subledgers, offering a reliable way to prioritize high-value transactions for review.
Random sampling
Random sampling selects a randomly chosen subset of records from a dataset. This approach is useful for unbiased testing or validation processes, ensuring each record has an equal probability of being included in the sample. It can be applied to both the general ledger and subledgers.
Systematic sampling
Systematic sampling selects records at regular intervals based on a predefined frequency (for example, every 10th record). This method ensures an evenly distributed sample across the dataset and can uncover patterns or anomalies within a dataset. It is particularly effective for structured financial reviews and can be applied to both the general ledger and subledgers for identifying irregularities in transaction posting or trends in financial data.
Generate a sample from analytic test results
To generate a sample from analytic test results:
-
Open the Analytics Hub. This can be done in two ways:
-
From the Documents page, click the Analytics icon (
 ) next to any checklist procedure where an analytic test is available. The Analytics tab will open providing a list of tests available for that checklist item.
) next to any checklist procedure where an analytic test is available. The Analytics tab will open providing a list of tests available for that checklist item. -
Select Analytics Hub at the top of the screen to display all checklist procedures that are available for an analytic test. Data must already be imported, or no data will be displayed.
2. Select an analytic test from the left panel. Results appear on the right. If there are no results, then run the analytic test first..
3. Select the Test parameters tab and scroll down to Sampling.
4. Select a Sampling method to apply to the selected analytic test results.
-
Attribute Sampling
-
Monetary Unit Sampling
-
Random Sampling
-
Systematic Sampling
Tip: You can adjust the parameters of the analytic test in the Configuration section to influence the sample results.
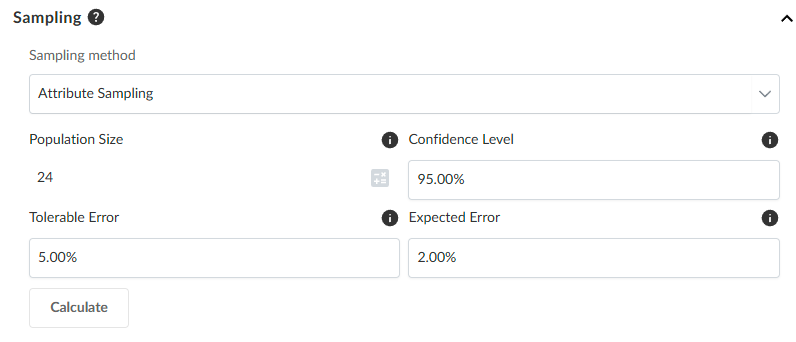
Generate an attribute sample from an analytic test
The sample calculator for Attribute Sampling includes specific calculator elements.
-
Follow the steps in Generate a sample from analytic test results and select Monetary Unit Sampling as your Sampling method.
-
Adjust your parmeters as needed. See Calculator parameters. Click Calculate
Calculator parameters
| Calculator parameter | Description |
|---|---|
| Population size | The total number of records available for sampling, based on the full dataset defined by the analytic tests selected and previously run. Select the Calculate Population Size icon ( This is required when:
|
| Confidence level | Specify the percentage certainty (for example, 90%, 95%) that you want to achieve in concluding that the control is effective. |
| Tolerable error | Enter the maximum percentage of control failures (for example, 5%) you are willing to accept while still considering the control effective. |
| Expected error | Estimate and enter the percentage of control failures (for example, 4%) you expect to find in the population based on prior audits or professional judgment. |
Tip: You can adjust the parameters of the analytic test in the Configuration section to influence the sample results.
The Sample size will generate in the fields below the Calculate button based on the selected analytic test results.
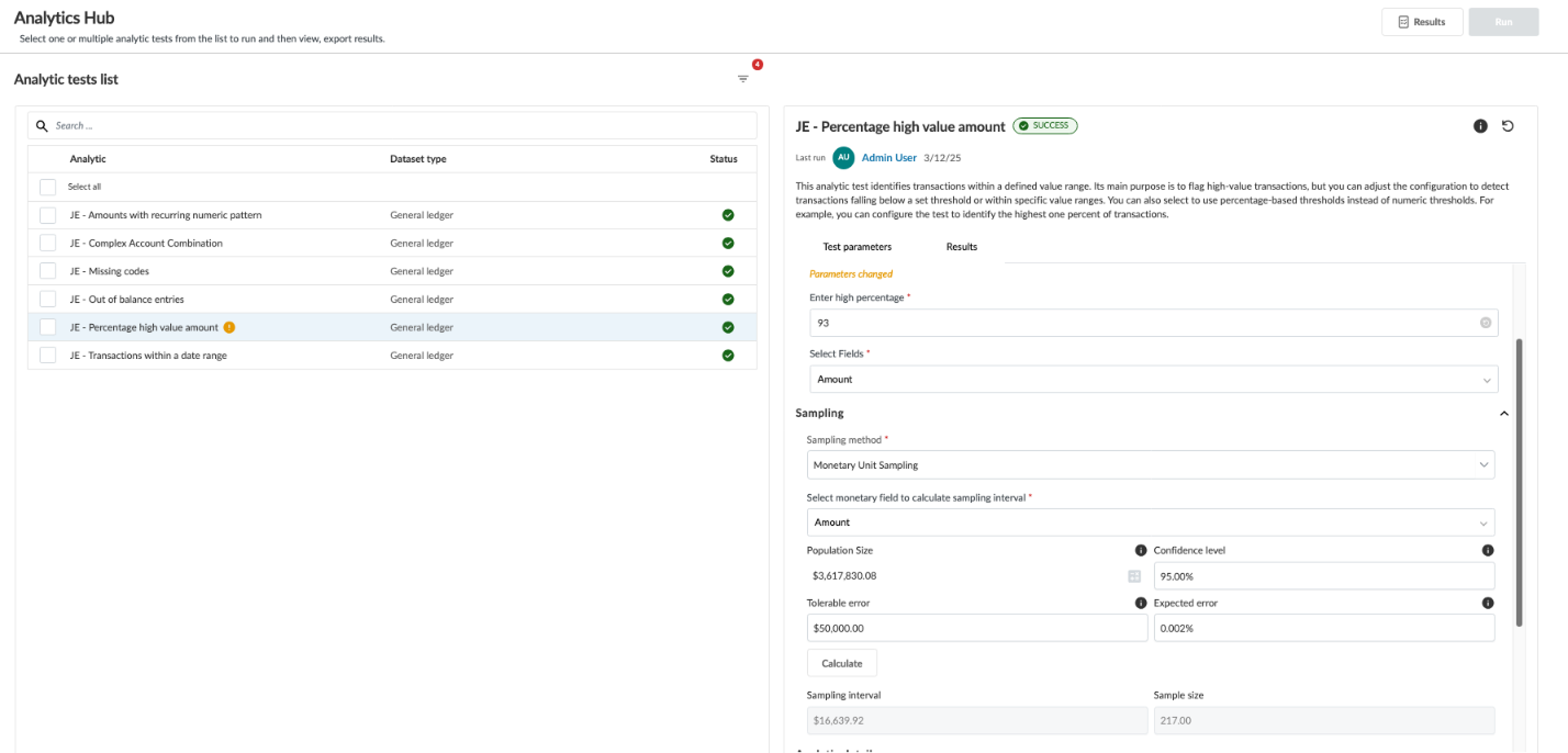
Generate a monetary unit sample from an analytic test
To generate a monetary unit sample from an analytic test:
The sample calculator for Monetary Unit Sampling includes specific calculator elements.
-
Follow the steps in Generate a sample from analytic test results and select Monetary Unit Sampling as your Sampling method.
-
On the right panel, in Select monetary field to calculate sampling interval, select Amount.
-
Adjust your parameters as needed and click Calculate.
Calculator parameters
| Calculator parameter | Description |
|---|---|
| Population size | The total number of records available for sampling, based on the full dataset defined by the analytic tests selected and previously run. Select the Calculate Population Size icon ( This is required when:
|
| Confidence level | Specify the desired level of assurance that the population is not misstated beyond the tolerable misstatement as a percentage. |
| Tolerable error | Specify the maximum amount of error or misstatement you are willing to accept in the population and still consider the financial statements to be fairly represented as a percentage. |
| Expected error | Specify your best estimate of the total misstatement in the population before testing as a percentage. |
Tip: You can adjust the underlying parameters of the analytic test and recalculate the population size.
The Sample size will generate in the fields below the Calculate button based on the selected analytic test results.
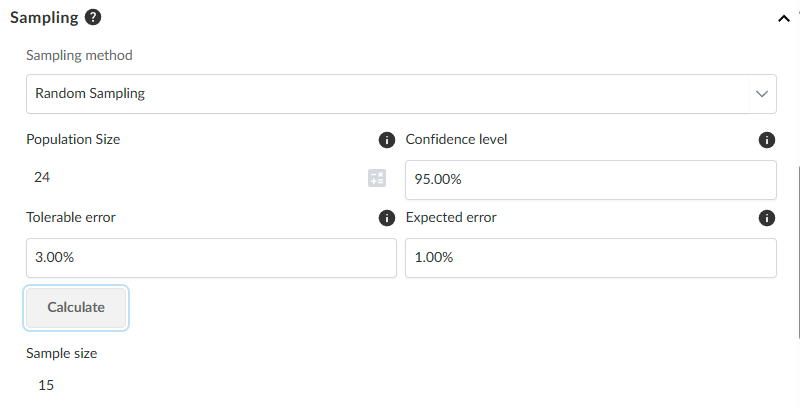
Generate a random sample from an analytic test
To generate a random sample from an analytic test:
The sample calculator for Random Sampling includes specific calculator elements.
-
Follow the steps in Generate a sample from analytic test results and select Random Sampling as your Sampling method.
-
Adjust your parameters as needed. See Calculator parameters. Click Calculate.
Calculator parameters
| Calculator parameter | Description |
|---|---|
| Population size | The total number of records available for sampling, based on the full dataset defined by the analytic tests selected and previously run. Select the Calculate Population Size icon ( This is required when:
|
| Confidence level | Specify the percentage confidence (for example, 90%, 95%) that the sample results will reflect the population accurately. |
| Tolerable error | Enter the maximum percentage of misstatements or anomalies (for example, 5%) you are willing to tolerate in the population. |
| Expected error | Provide your best estimate of the percentage of misstatements expected in the population before testing. |
Tip: You can adjust the underlying parameters of the analytic test and recalculate the population size.
The Sample size will generate in the fields below the Calculate button based on the selected analytic test results.
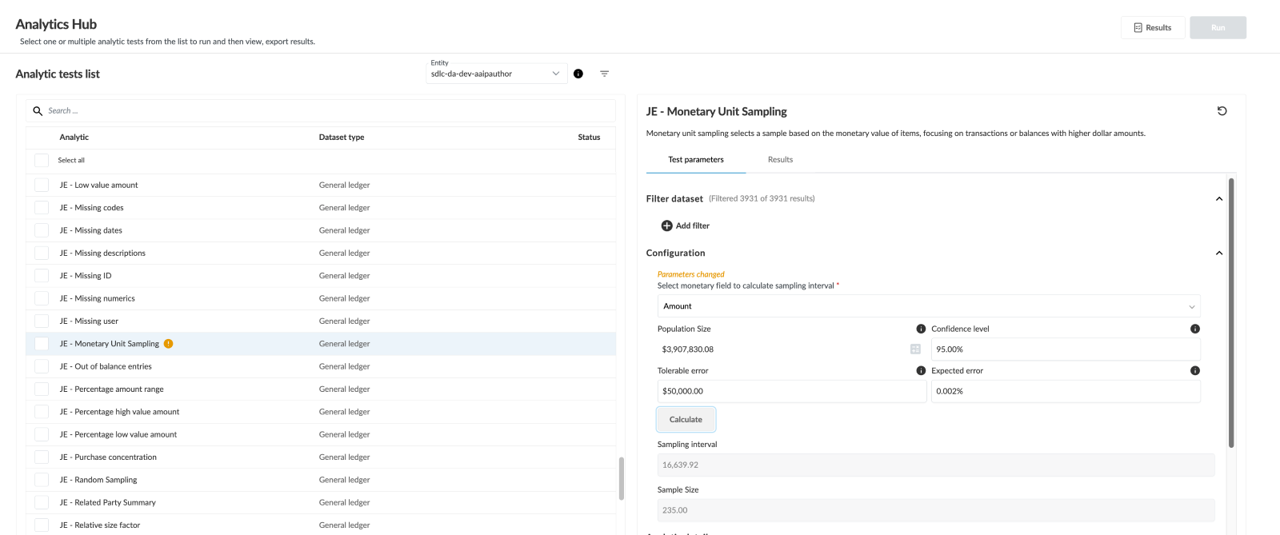
Generate a standalone sample from Analytics Hub
You can generate a standalone sample from Analytics Hub that is not based on an underlying analytic test but on the data imported into your engagement. A random, attribute, systematic or monetary unit sampling test can be selected from the left-side of Analytics Hub enabling you to generate a sample based on the population of the entire dataset or a customized filter.
Be sure you have imported the data required before calculating a standalone sample. The type of data required is listed under Dataset type. See Import the client's data from a CSV or Excel file for more information.
Example of the standalone Monetary Unit Sampling
Generate a standalone sample from schemaless data using Attribute or Random sampling methods
Schemaless data can be used to calculate standalone samples using the Attribute or Random sampling methods. Schemaless data refers to unstructured data that doesn’t follow a predefined format, for example, transaction data exported from a legacy system whose records do not have all the same fields, or whose structure is nested and inconsistent.
To begin, make sure you have imported the schemaless data you want to use into your engagement using the Other dataset type. See Import the client's data from a CSV or Excel file for more information.
-
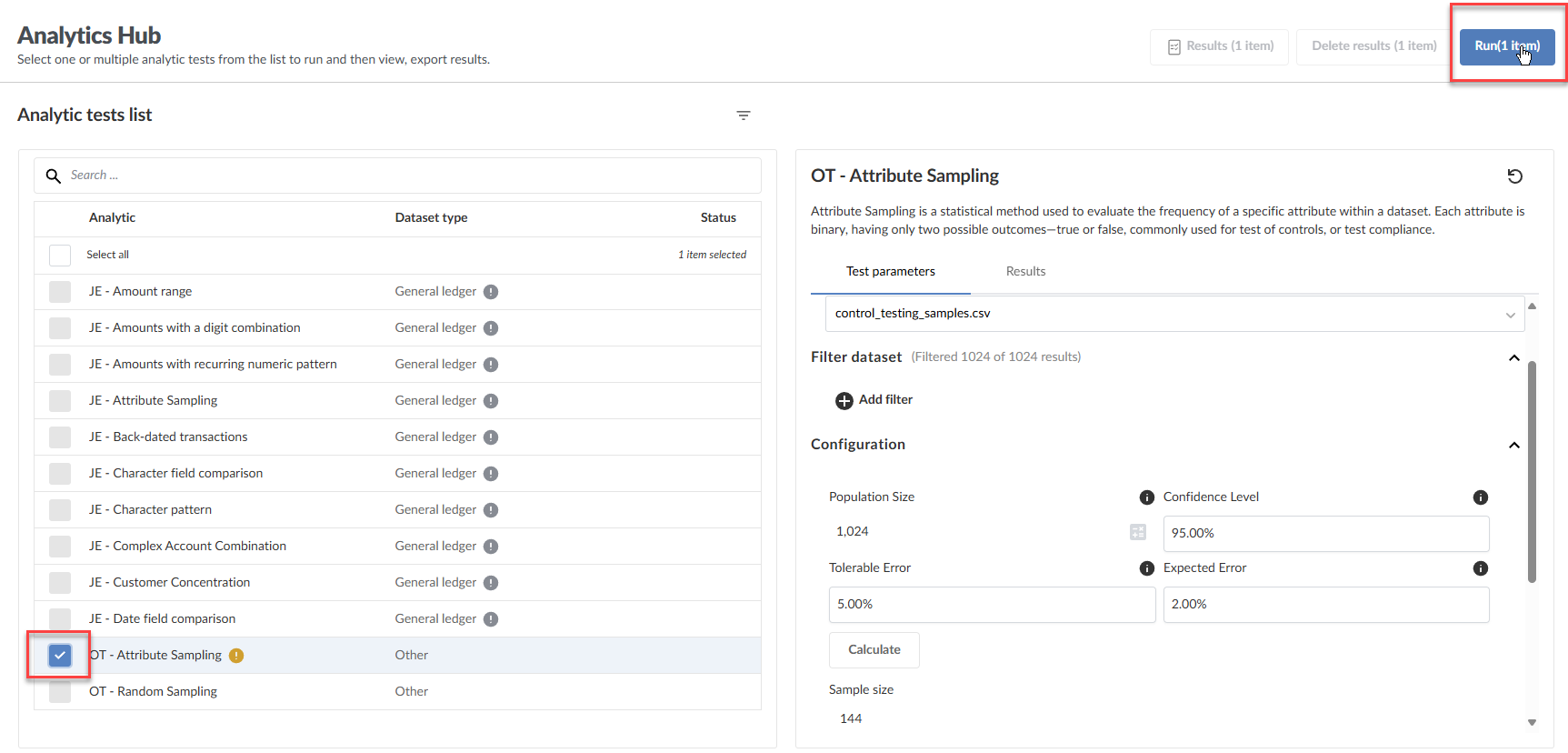
In the Analytics Hub, under Analytic tests list, select either the OT-Attribute Sampling or OT-Random Sampling methods.
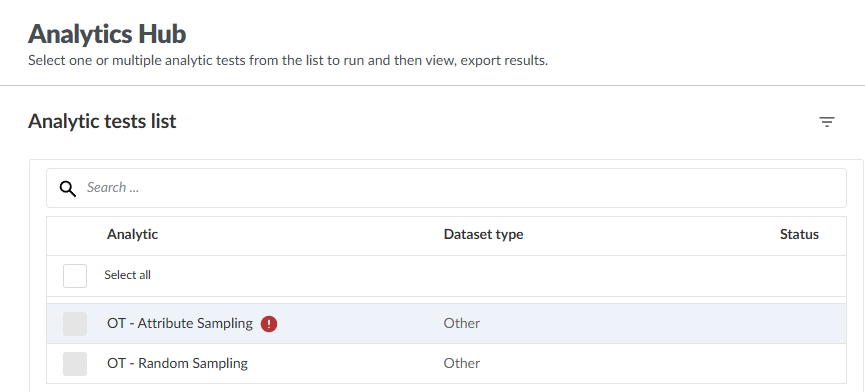
-
Select the Test parameters tab, and then in Dataset selection, select the source file containing the schemaless data you imported into your engagement previously.
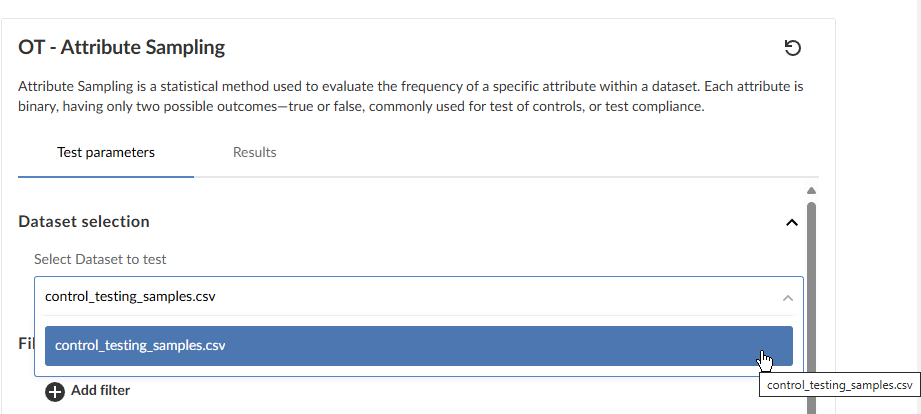
-
Under Configuration, specify values for the calculator parameters described in Calculator parameters.
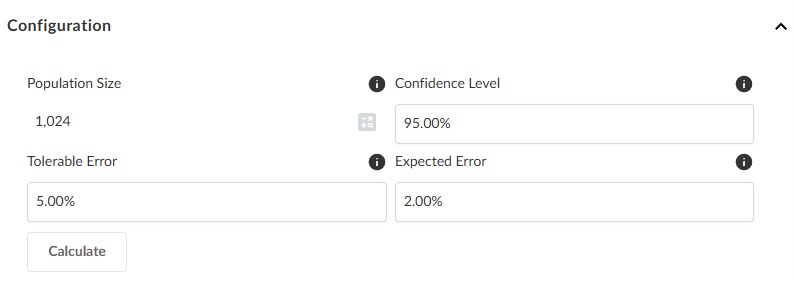
-
Click Calculate. The Sample size will generate in the fields below the Calculate button based on the schemaless data in your engagement.
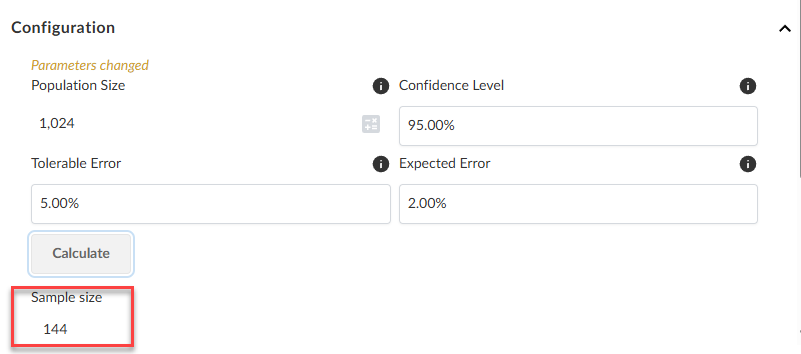
-
In Analytic tests list, select the checkbox for either the OT-Attribute Sampling or OT-Random Sampling method and then click Run in the top menu.
Calculator parameters
| Calculator parameter | Description |
|---|---|
| Population size | The total number of records available for sampling, based on the full dataset. Select the Calculate Population Size icon ( This is required when:
|
| Confidence level | Specify the desired level of assurance that the population is not misstated beyond the tolerable misstatement as a percentage: for example, 90%, 95%, or 99%. |
| Tolerable error | Specify the maximum amount of error or misstatement you are willing to accept in the population and still consider the financial statements to be fairly represented as a percentage. |
| Expected error | Specify your best estimate of the total misstatement in the population before testing as a percentage. This is often based on prior experience, historical data, or preliminary analysis. |
Export a sample
After you generate a data sample, you can export the sample to a CSV file by using the Export icon [![]() ] on the right-side of the analytic test in Analytics Hub.
] on the right-side of the analytic test in Analytics Hub.
